Congratulations to Rileigh for publishing her paper titled “Pulse Symmetry Impacts the C2 Product Selectivity in Pulsed Electrochemical CO2 Reduction” in ACS Energy Letters.
We have been fascinated with the concept of dynamic catalysis and exploiting resonances between applied modulations (e.g., electric field or strain) and microkinetic steps to impact overall catalytic activity and selectivity. We previously demonstrated that product selectivity of electrochemical CO2 reduction can be tuned by applying a square wave pulsed potential. Beyond modulating the frequency or amplitude of the square wave, changing the waveform presents an interesting, previously unexplored, parameter to gain new mechanistic insights and further advance control over product selectivity.
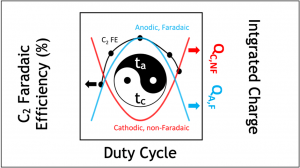
Rileigh’s paper describes our systematic examination of the effects of pulse potential, duration, and profile symmetry on the resulting products from electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Our study provides new physical insight into the role of co-adsorbed ions, interfacial charge, and changing electric field at the reaction interface on C-C coupling. Our in-depth analysis of transient charge transfer processes provides new understanding of the role of programmed potential pulses on improved C2 product selectivity. We show, for the first time, that symmetric pulse shapes optimize C2 selectivity, which we attribute to balancing of microkinetic steps and optimization of the the local reaction environment for C-C coupling through electrolyte ion co-adsorption and electric field effects.

